Digital Accountability: Harnessing Photo Forensics for e-Services Audits By Mr. Virender Kulharia, Director
Introduction
In an era where technology intertwines with governance, the shift towards online portals for delivering public services has been monumental. Governments are leveraging digital platforms to streamline processes, enhance accessibility, and ensure efficient delivery of welfare schemes. From social security benefits to healthcare subsidies, citizens now have the convenience of submitting required documents online, eliminating the hassles of physical paperwork.
As per the “National e-Governance Service Delivery Assessment (NeSDA) - Way Forward Monthly Report1 of March 2024 produced by the Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DARPG), Departments across States/UTs provide 16,517 e-services to citizens and businesses. Tamil Nadu topped all states by offering 1,128 e-services. The report underscores the sectoral dominance of Local Governance & Utility Services, with 5,288 e-services. Furthermore, States such as Tamil Nadu, Jammu and Kashmir, Kerala, Assam, and Odisha have achieved complete service delivery integration through unified portals like tnesevai, e-UNNAT, e-Sevanam, Sewa Setu, and Odisha One. The report also highlights Goa Online, Aaple Sarkar (Maharashtra), e-District (Chhattisgarh), MeeSeva (Telangana), e-District (A&N Islands), and e-District (Bihar). However, as governments embrace digitalization, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of the submitted documents becomes paramount. The transition to digital platforms brings forth a new set of challenges, particularly concerning document verification and consequently the need for better audit procedures. There has been a proliferation of photo-editing tools over the past decade. Some highly regarded tools for their features and ease of use include Pixlr, GIMP, Canva, Fotor, Adobe Photoshop Express, Adobe Lightroom, etc. With ease of manipulating digital images, the risk of fraudulent submissions is high. For instance, to qualify for housing assistance programs, individuals/agency may submit edited photographs. For releasing funds from Escrow Account, a builder/promoter could submit edited CA certificate to RERA.

Figure 1 : AI generated representative image
Case Study from BOCW Audit
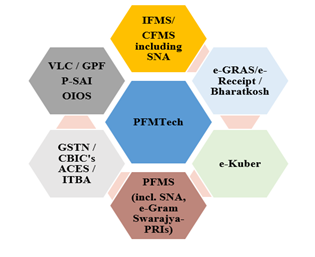
Section 12 of the BOCW Act provides that every building worker, engaged in any building or other construction work for not less than ninety days during the preceding 12 months, shall be eligible for registration as a beneficiary under this Act. The Board integrated (December 2018) the registration process of beneficiaries with Antyodaya SARAL Platform (Unified Portal) making it mandatory for construction workers to apply for registration through online portal of Antyodaya SARAL Platform only. The process for online submission of application is given below:

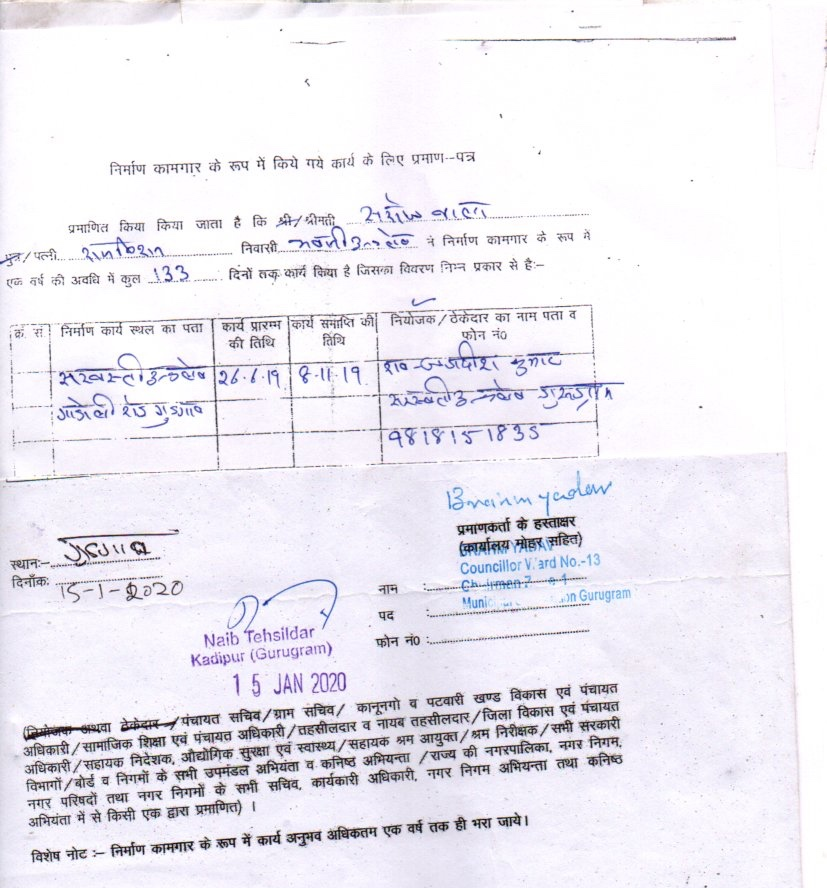
While reviewing the work-slips uploaded by the beneficiaries on the portal, audit observed that some of the work-slips were edited or manipulated. These beneficiaries had obtained benefits in lakhs. To verify the genuineness of these work slips, Audit used Photo Forensic Techniques. The techniques used by audit are described below:
1. Error Level Analysis (ELA): It involves analyzing the error levels within an image to detect areas that have been modified or edited. The underlying principle of ELA is based on the observation that when an image is edited, the compression algorithm used to save the image can introduce different levels of error. This tool compares the original image to a recompressed version. This can make manipulated regions stand out in various ways. For example, they can be darker or brighter than similar regions which have not been manipulated. Example from an edited work-slip found in BOCW Audit is as below:
| Cropped area of uploaded work-slip | Error Level Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
The above analysis indicates evidence of signature copying and pasting that is imperceptible to the naked eye.
2. Noise Analysis: Digital images captured by cameras or created through digital manipulation processes contain inherent noise, which is a random variation in pixel values caused by factors such as sensor imperfections, electrical interference, or image compression. This tool basically a reverse denoising algorithm. Rather than removing the noise it removes the rest of the image. It is using a super simple separable median filter to isolate the noise. It is used for identifying manipulations to the image like airbrushing, deformations, warping and perspective corrected cloning. Example from an edited work-slip found in BOCW Audit is as below:
| Work slip document uploaded | Noise analysis of the document |
 |
 |
As can be seen from above, the noise in the lower part of the document is markedly different from the upper half indicating manipulation. This indicate superimposition of two different documents or images.
3. Principal Component Analysis: This tool performs principal component analysis on the image. This provides a different angle to view the image data which makes discovering certain manipulations & details easier. PCA is employed as a statistical tool to analyze and process digital images for various purposes, such as image enhancement, feature extraction, and manipulation detection. PCA works by transforming a dataset of possibly correlated variables (in this case, image pixels) into a new set of uncorrelated variables called principal components. These principal components are linear combinations of the original variables and are ordered in such a way that the first component captures the maximum variance in the data, the second component captures the maximum remaining variance, and so on.
| Work slip document uploaded | PCA of the document |
 |
 |
A few cases where the techniques demonstrated tampering or manipulation of work-slips are shown in Annexure- Examples comprising with all the three techniques applied on each one of them.
Other Photo Forensic Techniques
Apart from these three methods, there are several other techniques, which could be applied to detect manipulation in images. These include Clone Detection, Luminance Gradient, Meta Data, Geo Tags, Thumbnail Analysis, JPEG Analysis and String Extraction. The clone detector highlights similar regions within an image. These can be a good indicator that a picture has been manipulated using the clone tool.
The luminance gradient tool analyses the changes. Parts of the image which are at a similar angle (to the light source) and under similar illumination should have a similar color. Similar edges should have similar gradients. If the gradients at one edge are significantly sharper than the rest, it is a sign that the image could have been copy pasted. It does also reveal noise and compression artefacts quite well.
Metadata analysis provides valuable insights by uncovering hidden information embedded within images. EXIF (Exchangeable image file format) metadata contains a variety of details about the image and its creation. This includes Camera Information, Date and Time, Software Details: Applications used to edit or process the image, such as Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, or others, GPS Coordinates: Location data of where the image was taken, if available. An image's EXIF data might reveal that it was created using Adobe Photoshop CS6, which suggests that it may have been digitally altered. A photo taken supposedly in remote location might reveal geotag coordinates that place it in a completely different area, suggesting the image may not be genuine. Many digital cameras embed a thumbnail preview image within the original photo file. This preview is often stored to allow quick display without processing the full-size image. Thumbnail analysis could uncover a different scene than the displayed full-size photo, indicating possible manipulation or tampering.
Limitations of Photo Forensic Techniques
While using Photo Forensic tools, it is important to remember that these tools function much like a magnifying glass. They help reveal details that are otherwise hidden, allowing us to uncover potential manipulations. However, just as a magnifying glass does not reveal the absolute truth but aids in uncovering it, photo forensics tools provide insights that need to be interpreted carefully. It is also crucial to remember that the absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, and extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence. Therefore, while these tools are powerful, they must be used judiciously and in conjunction with other verification methods to draw reliable conclusions.
Exploring Scalability and Efficiency
To execute these analyses, we utilized the resources of a free website, https://29a.ch/photo-forensics/#forensic-magnifier, which hosts a suite of tools for digital image forensics. This website operates offline, ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive images by enabling local processing without the need for external sharing. However, the website allows for the analysis of images individually and does not automatically highlight problematic areas. It is for the user to interpret the results and identify any potential issues within the images. While considering the scalability and efficiency of our approach, we explored batch processing of all beneficiary documents. However, we concluded that the responsibility for implementation lies with the Department concerned. Nevertheless, our research indicated that Google Cloud Platform offers a cost-effective and expeditious solution in this regard. Leveraging Google Cloud Platform's Document AI service, departments can automate document-related tasks, enhance data extraction, and derive deeper insights from both structured and unstructured document information. Document AI facilitates the creation of high-accuracy processors for document extraction, classification, and splitting.
Complementing Document AI, Google's Cloud Vision API is also important. This tool harnesses advanced vision models via APIs, automating vision tasks, streamlining analysis, and unlocking actionable insights. Similar services are offered by Microsoft Azure and Amazons AWS and could be explored for implementation.

Figure 2: Representative Image for Cloud Platforms
Conclusion
In advocating for the broader adoption of Photo Forensics tools, the importance is not only underscored in audits but also in governmental processes. By detecting fraudulent submissions, these techniques ensure that welfare benefits or e-services reach deserving recipients, thereby upholding the credibility and efficacy of government programs. As such, the incorporation of Photo Forensics is recommended into the toolkit of Government Departments, reinforcing transparency and accountability in service delivery.
As governments continue to embrace digital transformation in service delivery, integrating robust mechanisms such as Photo Forensics becomes imperative. By leveraging technology to uphold the integrity of welfare schemes, administrations can uphold principles of fairness, equity, and efficiency.
Example 1
| Work slip document uploaded | Error Level Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
| Noise analysis of the document | Principal Component Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
Example 2
| Work slip document uploaded | Error Level Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
| Noise analysis of the document | Principal Component Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
Example 3
| Work slip document uploaded | Error Level Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
| Noise analysis of the document | Principal Component Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
Example 4
| Work slip document uploaded | Error Level Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
| Noise analysis of the document | Principal Component Analysis of the document |
 |
 |
Continue Reading

From the Editor's Desk
Forty years ago, recognising the knowledge driven nature of our Institution, the quarterly publication of the “Journal of Management and Training” was initiated....

Reporting for impact - Improving readability of audit reports
The need for enhancing the value and impact of CAG’s audit has been an enduring concern...

Application of Machine Learning Algorithms in Audit
There has been a tremendous explosion of data available with public sector entities over the last 20 years...

Accessibility of Cutting-Edge Technologies in GIS and RS
The democratization of cutting-edge technologies such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Remote Sensing stands as a huge shift, empowering...
Beneficiaries of Social Schemes and Assessment
Social programmes have evolved over the decades, aiming for increased coverage, higher entitlements, and better design by using technology for targeting...

Blue Carbon Accounting
Human beings thrive in diverse ecosystems but often simplify these ecosystems over time. This simplification occurs through targets...

Generative AI: The Age of Artificial Imagination
In the vast landscape of artificial intelligence, few innovations have captured the imagination of the humans and sparked as much excitement as...

A 1.5-year-old DAG in a 150-year-old Institution
It was on 14th December 2022 when our posting orders came while I was still attached as an Assistant Director in the CRA Wing in the Headquarters Office, New Delhi....

Water Resource Accounting in India
Water: The word itself is an indication of life on the planet. About 60% of the human body contains water...